Gloeckner et al, Methods Mol Biol, 2009
Tandem Affinity Purification (TAP)
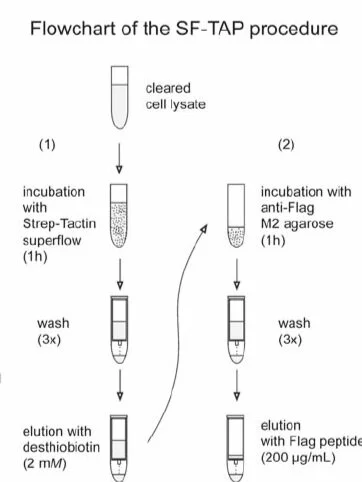
TAP is an affinity purification strategy for the efficient isolation and characterization of native protein complexes. Isolation and dissection of native multiprotein complexes is a central theme in functional genomics. The development of the tandem affinity purification (TAP) tag has enabled an efficient and large-scale purification of native protein complexes. The original TAP tag features a size of 21 kDa and requires time consuming cleavage. By combining a tandem Strep-tag II with a FLAG-tag , the size of the TAP (SF-TAP) tag is reduced to to 4.6 kDa. Both tags have a medium affinity and avidity to their immobilized binding partners. This allows the elution of SF-tagged proteins under native conditions using desthiobiotin in the first step and the FLAG octapeptide in the second step. The SF-TAP protocol represents an efficient, fast and straightforward purification of protein complexes from mammalian cells.